Peter Lobner, 19 March 2025
The Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT), is a microwave wavelength telescope located in the Atacama Desert in Chile, at an altitude of 5,190 meters (17,030 ft), making it one of the highest ground-based telescopes in the world. ACT took its final data in 2022 and has since been decommissioned.



Sources: (top) NDRIO White Paper, A. Hicks, 2020, (middle) Wikipedia, (bottom) flickr
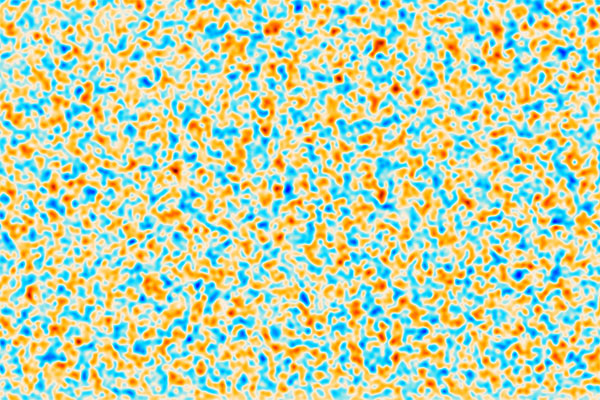
The Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT) Collaboration posted new maps of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation based on the final data collected with the Advanced ACT camera over the period 2017–2022. The CMB is the light released from the primordial universe as atoms first started forming and space became transparent, approximately 380,000 years after the Big Bang. The new maps cover 19,000 square degrees, almost one-half of the total area of the celestial sphere, which measures about 41,253 square degrees.
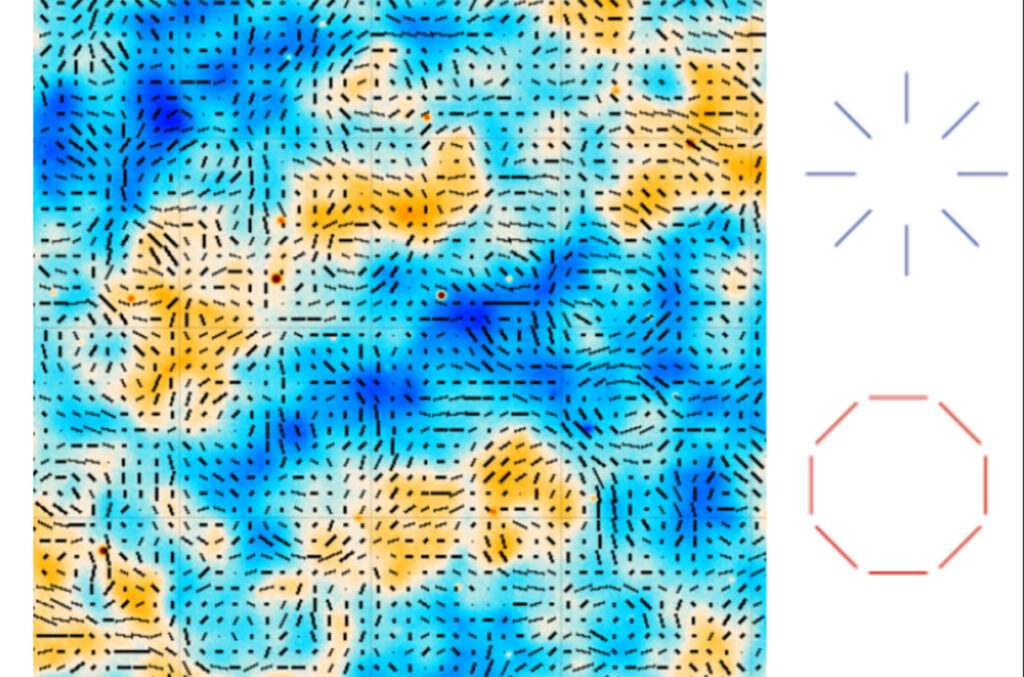
how polarization reveals the movement of primordial gases.
Source: ACT Collaboration
For more information on the new ACT maps, see the following article in Science:
- Daniel Clery, “This is the sharpest image yet of our universe as a baby – The Atacama Cosmology Telescope captures the afterglow of the Big Bang in unprecedented detail,” Science, 18 Mar 2025: https://www.science.org/content/article/sharpest-image-yet-our-universe-baby
The complete ACT data release papers are listed here: https://act.princeton.edu
The new CMB map shown above is described in detail here:
- S. Naess, et al., “The Atacama Cosmology Telescope: DR6 Maps,” Draft preprint, March 18, 2025: https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fo/iwdx2rg6z66qzteq1yhob/AEW-rphyTGa91S_TFMu02DQ?e=2&preview=act_dr6_maps.pdf&rlkey=nvjg4wwd1z1pilheladjf0068&st=x1a6kx5y&dl=0